Back Pain Treatment
In addressing back pain, our Interventional Spine and Pain Clinic stands out with a specialized treatment that combines precision and innovation. Rather than merely managing symptoms, our clinic focuses on targeted interventions like epidural steroid injection, endoscopic spine procedure, Laser disc treatment , spinal cord stimulator like advanced procedures that directly address the underlying causes of back pain. Our physician employs state-of-the-art, minimally invasive procedures designed to provide not only prompt relief but also long-term results. From herniated discs to spinal stenosis, our personalized approach ensures that each patient receives a tailored treatment plan, optimizing outcomes and minimizing the impact of back pain on daily life. Choose our Interventional Spine and Pain Clinic for a unique and effective solution to back pain, where expertise meets a commitment to lasting relief.
Book An Appointment
Fill out the form below or call us at +971 50 480 4987 or email us at [email protected] to book an appointment with us.
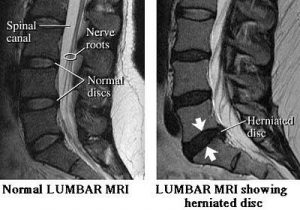
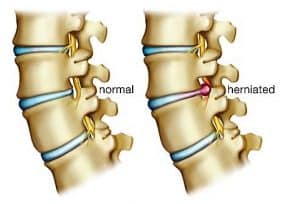
Slip Disc
Although people often refer to a disc herniation as a slipped disc, the disc doesn’t actually slip out of place. Rather, the term herniation means that the material at the center of the disc has squeezed out of its normal space. Herniation occurs when the nucleus in the center of the disc pushes out of its normal space. The nucleus presses against the annulus, causing the disc to bulge outward. Sometimes the nucleus herniates completely through the annulus and squeezes out of the disc.
Sciatica / Lumbar Radiculopathy
The term sciatica describes the symptoms of leg pain—and possibly tingling, numbness, or weakness – that originate in the lower back and travel through the buttock and down the large sciatic nerve in the back of each leg. Sciatica is not a medical diagnosis in and of itself—it is a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Common lower back problems that can cause sciatica symptoms include a lumbar herniated disc, degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, or spinal stenosis.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a broad term that simply refers to some type of degeneration in the spine. Most often, the term spondylosis is used to describe osteoarthritis of the spine, but it is also commonly used to describe any manner of spinal degeneration. As with many other terms to describe spinal problems, spondylosis is more of a descriptive term than it is a clinical diagnosis.
The patient may have pain from facet joint osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis (an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal, which is creating leg pain when the patient walks) or could be caused by degenerative disc disease, in which a degenerated disc that becomes dehydrated and loses some of its function. The degenerated disc can cause low back pain or neck pain, and possibly leg pain or arm pain.

Disc Bulge
Bulging discs, also known as a disc protrusion, are a very common occurrence. They usually remain asymptomatic; however, they can cause discomfort and disability in various parts of the body if the disc compresses an adjacent nerve root or the spinal cord. As we age, the outer fibrous portion of our discs can weaken. Pressure from the central core of the disc can then stretch to the outer rim, causing the disc to bulge. If left untreated, the disc can continue to bulge until it tears, which is classified as a herniated disc. Because a bulging disc does not always show symptoms, many people have bulging discs without realizing it. As long as the bulging area does not press against a nearby nerve, no symptoms occur. When the bulging disc does cause a pinched nerve, you may begin to experience symptoms.
Spinal Stenosis
In the medical field, stenosis means the abnormal narrowing of a body channel. When combined with the word spinal, it defines a narrowing of the bone channel occupied by the spinal nerves or the spinal cord. Some people are born with a congenital form, but most develop spinal stenosis as part of the degenerative cascade. A few do not feel any effects of the narrowing, but as part of the aging process, most people will eventually notice radiating pain, weakness, and/or numbness secondary to the compression of the nerves or spinal cord. While the narrowing may occur at different parts of the spine, the symptoms of nerve compression are often similar. That is why specialists often will perform testing to determine the cause and location of the narrowing.
Pain after spinal surgery
Post-Laminectomy Syndrome (PLS), also known as failed back syndrome, describes a chronic, painful condition that some patients after undergoing back surgery, specifically a laminectomy or microdiscectomy. Post-Laminectomy Syndrome is not a diagnosis, but rather a general term to describe a variety of chronic pain syndromes experienced by patients as they emerge from back surgery. The exact cause of Post-Laminectomy Syndrome is unknown, however one prominent theory points to epidural fibrosis, in which the development of scar tissue during post-surgical healing compresses nearby nerve roots and causes pain.
Spine Joints pain
Spinal arthritis causes stiffness and low back pain. The stiffness is worst upon waking up in the morning, tends to ease with activity and then worsens toward the end of the day. Presumably, this is because fluid has built up in the joint due to inactivity overnight, which causes more swelling.
The low back pain due to spine joint arthritis has a typical pattern:
- The pain is mostly in the back, runs into the buttocks, and often really feels like it’s in the hip.
- As it gets even worse people often report burning on the outer aspect of the thigh, and sometimes pain down the leg.
- Because the pain runs down the leg people, even doctors sometimes, confuse it with nerve root pain.
Disc Degenerative Disease
Disc degenerative disease refers to symptoms of back or neck pain caused by wear-and-tear on a spinal disc. In some cases, degenerative disc disease also causes weakness, numbness, and hot, shooting pains in the arms or legs (radicular pain). Degenerative disc disease typically consists of a low-level chronic pain with intermittent episodes of more severe pain. Painful disc degeneration is common in the neck (cervical spine) and lower back (lumbar spine). These areas of the spine undergo the most motion and stress, and are most susceptible to disc degeneration.
Facet Arthritis
Facet joint arthropathy refers to a degenerative disease that affects the joints of the spine and the breakdown of cartilage on those joints. Facet joint arthropathy can go by other names, such as facet joint arthrosis or, most commonly, facet joint osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is one of many types of arthritis. There are actually more than 100 different types of arthritis in existence but osteoarthritis is the most widespread. Generally speaking, osteoarthritis is the result of normal age-related degeneration.

Spondylolysis/Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolysis is a crack or stress fracture in one of the vertebrae, the small bones that make up the spinal column. The injury most often occurs in children and adolescents who participate in sports that involve repeated stress on the lower back, such as gymnastics, football, and weight lifting.In some cases, the stress fracture weakens the bone so much that it is unable to maintain its proper position in the spine—and the vertebra starts to shift or slip out of place. This condition is called spondylolisthesis.Patients who have persistent back pain or severe slippage of a vertebra, however, may need surgery to relieve their symptoms and allow a return to sports and activities.
Failed back surgery syndrome
Failed back surgery syndrome(FBSS), also known as post-laminectomy syndrome, describes a chronic, painful condition that some patients after undergoing back surgery, specifically a laminectomy or microdiscectomy. Failed back surgery syndrome Syndrome is not a diagnosis, but rather a general term to describe a variety of chronic pain syndromes experienced by patients as they emerge from back surgery. The exact cause of FBSS is unknown, however one prominent theory points to epidural fibrosis, in which the development of scar tissue during post-surgical healing compresses nearby nerve roots and causes pain.
Spinal compression fractures
The type of fracture in the spine that is typically caused by osteoporosis is generally referred to as a compression fracture. A compression fracture is usually defined as a vertebral bone in the spine that has decreased at least 15 to 20% in height due to fracture.These compression fractures can occur in vertebrae anywhere in the spine, but they tend to occur most commonly in the upper back (thoracic spine), particularly in the lower vertebrae of that section of the spine (e.g. T10, T11, T12). They rarely occur above the T7 level of the spine. They often occur in the upper lumbar segments as well, such as L1.

Spinal involvement with cancer
Cancers that form in other parts of the body have a tendency to spread, or metastasize, to the spine. When this happens, the cancer weakens the spine bones, making them susceptible to compression fractures. Doctors may suspect unrecognized cancer if a patient has a compression fracture without any particular cause or reason.
Pain of spinal cord injury, quadriplegia, and paraplegia
Pain is a serious problem for many people with spinal cord injuries (SCI). Pain after SCI can occur in parts of the body where there is normal sensation (feeling) as well as areas that have little or no feeling. The majority of people with SCI report that they have chronic pain. Chronic pain is pain that does not go away and instead lasts months to years. The cause of the pain may be unknown but is most often related to nerve damage from the SCI or musculoskeletal problems that arise in dealing with an SCI. The pain can come and go. Chronic pain is difficult to completely eliminate but often can be managed or reduced enough so that it doesn’t overwhelm your life.
Sacroiliac joint pain
The term sacroiliitis is used to describe any inflammation in the sacroiliac joint, which is located on either side of the sacrum (lower spine) that connects to the iliac bone in the hip. Sacroiliitis is often found as part of a feature of inflammatory conditions of the spinal column. As a group, these conditions and diseases are termed a “spondyloarthropathy” and include conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis, among others. Sacroiliitis is also a term that is sometimes used interchangeably with the term sacroiliac joint dysfunction, as technically either term can be used to describe pain that stems from the sacroiliac joint (or SI joint).
Piriformis syndrome
Piriformis syndrome is a condition in which the piriformis muscle, located in the buttock region, spasms and causes buttock pain. The piriformis muscle can also irritate the nearby sciatic nerve and cause pain, numbness and tingling along the back of the leg and into the foot (similar to sciatic pain).

Dr. Manish Raj
MD, DA(Gold Medal), FENDS, FIAPM, FISP, FPM
MEET YOUR DOCTOR
Read Our Patient Opinion
OUR AFFILIATIONS







